PHOTOFRIN is a photoactivated radical generator indicated for palliation of patients with completely obstructing esophageal cancer, or of patients with partially obstructing esophageal cancer who, in the opinion of their physician, cannot be satisfactorily treated with Nd:YAG laser therapy
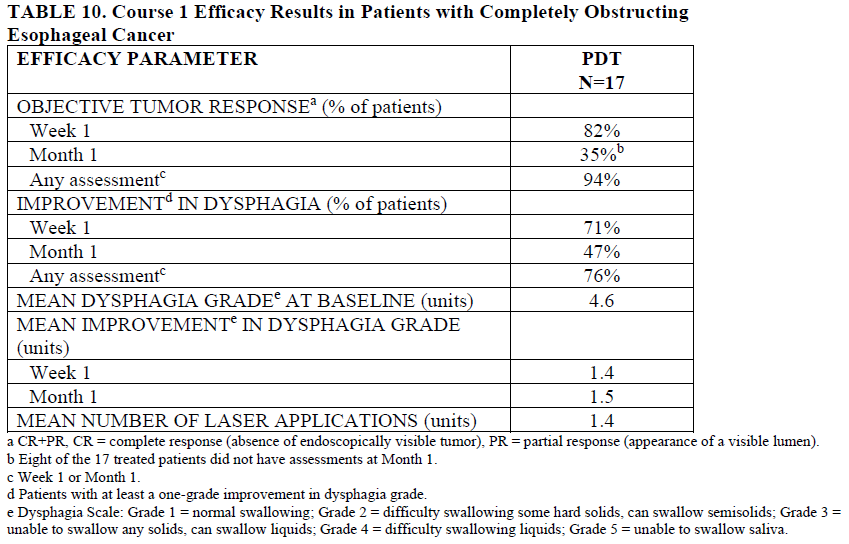
In a multicenter, single-arm study in 17 patients with completely obstructing esophageal carcinoma treated with PDT with PHOTOFRIN, after a single course of therapy, 94% of patients obtained an objective tumor response and 76% of patients experienced some palliation of their dysphagia.
Course 1 Efficacy Results in Patients with Completely Obstructing Esophageal Cancer
| EFFICACY PARAMETER | PDT N=17 |
|---|---|
| OBJECTIVE TUMOR RESPONSEa (% of Patients) | |
| Week 1 | 82% |
| Month 1 | 35%b |
| Any assessmentc | 94% |
| IMPROVEMENTd IN DYSPHAGIA (% of Patients) | |
| Week 1 | 71% |
| Month 1 | 47% |
| Any assessmentc | 76% |
| MEAN DYSPHAGIA GRADEe AT BASELINE (units) | 4.6 |
| MEAN IMPROVEMENTe IN DYSPHAGIA GRADE (units) | |
| Week 1 | 1.4 |
| Month 1 | 1.5 |
| MEAN NUMBER OF LASER APPLICATIONS (units) | 1.4 |
aCR+PR, CR = complete response (absence of endoscopically visible tumor), PR = partial response (appearance of a visible lumen).
bEight of the 17 treated patients did not have assessments at Month 1.
cWeek 1 or Month 1.
dPatients with at least one-grade improvement in dysphagia grade.
eDysphagia Scale: Grade 1 = normal swallowing; Grade 2 = difficulty swallowing some hard solids, can swallow semisolids; Grade 3 = unable to swallow any solids, can swallow liquids; Grade 4 = difficulty swallowing liquids; Grade 5 = unable to swallow saliva.
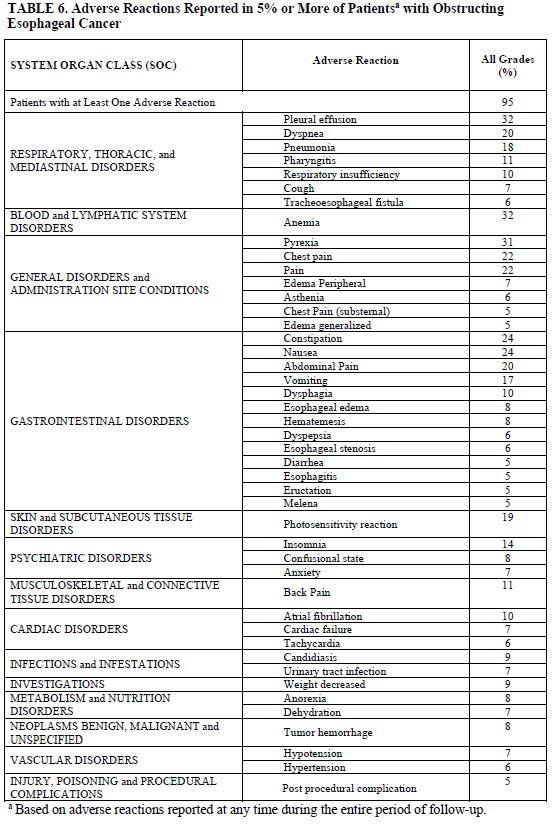
Adverse Reactions Reported in 5% or More of Patientsa with Obstructing Esophageal Cancer
| SYSTEM ORGAN CLASS (SOC) | Adverse Reaction | All grades (%) |
|---|---|---|
| Patients with at Least One Adverse Reaction | 95 | |
| RESPIRATORY, THORACIC and MEDIASTINAL DISORDERS | Pleural effusion | 32 |
| Dyspnea | 20 | |
| Pneumonia | 18 | |
| Pharyngitis | 11 | |
| Respiratory insufficiency | 10 | |
| Cough | 7 | |
| Tracheoesophageal fistula | 6 | |
| BLOOD and LYMPHATIC SYSTEM DISORDERS | Anemia | 32 |
| GENERAL DISORDERS and ADMINISTRATION SITE CONDITIONS | Pyrexia | 31 |
| Chest Pain | 22 | |
| Pain | 22 | |
| Edema Peripheral | 7 | |
| Asthenia | 6 | |
| Chest Pain (substernal) | 5 | |
| Edema Generalized | 5 | |
| GASTROINTESTINAL DISORDERS | Constipation | 24 |
| Nausea | 24 | |
| Abdominal Pain | 20 | |
| Vomiting | 17 | |
| Dysphagia | 10 | |
| Esophageal Edema | 8 | |
| Hematemesis | 8 | |
| Dyspepsia | 6 | |
| Esophageal Stenosis | 6 | |
| Diarrhea | 5 | |
| Esophagitis | 5 | |
| Eructation | 5 | |
| Melena | 5 | |
| SKIN and SUBCUTANEOUS TISSUE DISORDERS | Photosensitivity reaction | 19 |
| PSYCHIATRIC DISORDERS | Insomnia | 14 |
| Confusional state | 8 | |
| Anxiety | 7 | |
| MUSCULOSKELETAL and CONNECTIVE TISSUE DISORDERS | Back Pain | 11 |
| CARDIAC DISORDERS | Atrial fibrillation | 10 |
| Cardiac failure | 7 | |
| Tachycardia | 6 | |
| INFECTIONS and INFESTATIONS | Candidiasis | 9 |
| Urinary tract infection | 7 | |
| INVESTIGATIONS | Weight decreased | 9 |
| METABOLISM and NUTRITION DISORDERS | Anorexia | 8 |
| Dehydration | 7 | |
| NEOPLASMS BENIGN, MALIGNANT and UNSPECIFIED | Tumor hemorrhage | 8 |
| VASCULAR DISORDERS | Hypotension | 7 |
| Hypertension | 6 | |
| INJURY, POISING and PROCEDURAL COMPLICATIONS | Post procedural complication | 5 |
aBased on adverse reactions reported at any time during the entire period of follow-up.
IMPORTANT SAFETY INFORMATION
Esophageal Cancer
PHOTOFRIN® is indicated for the palliation of patients with completely obstructing esophageal cancer, or of patients with partially obstructing esophageal cancer who, in the opinion of their healthcare provider, cannot be satisfactorily treated with Nd:YAG laser therapy.
Endobronchial Cancer
PHOTOFRIN is indicated for the treatment of microinvasive endobronchial non-small-cell lung cancer (NSCLC) in patients for whom surgery and radiotherapy are not indicated.
PHOTOFRIN is indicated for the reduction of obstruction and palliation of symptoms in patients with completely or partially obstructing endobronchial NSCLC.
High-Grade Dysplasia in Barrett’s Esophagus
PHOTOFRIN is indicated for the ablation of high-grade dysplasia in Barrett’s esophagus patients who do not undergo esophagectomy.
IMPORTANT WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS USING PHOTOFRIN® INCLUDE:
Gastroesophageal Fistula and Perforation: Do not initiate PHOTOFRIN with photodynamic therapy (PDT) in patients with esophageal tumors eroding into the trachea or bronchial tree or bronchial wall.
Pulmonary and Gastroesophageal Hemorrhage: Assess patients for tumors eroding into a pulmonary blood vessel and esophageal varices. Do not administer light directly to an area with esophageal varices.
High-Grade Dysplasia (HGD) in Barrett’s Esophagus (BE): After treatment of HGD in BE, conduct endoscopic biopsy surveillance every 3 months, until 4 consecutive negative evaluations for HGD have been recorded.
Photosensitivity and Ocular Photosensitivity: Observe precautions to avoid exposure of skin and eyes to direct sunlight or bright indoor light for at least 30 days. Instruct patients when outdoors to wear dark sunglasses which have an average light transmittance of <4% for at least 30 days and until ocular sensitivity resolves.
Use Before or After Radiotherapy: Allow 2-4 weeks between PDT and subsequent radiotherapy.
Chest Pain: Substernal chest pain can occur.
Airway Obstruction and Respiratory Distress: Administer with caution to patients with tumors in locations where treatment-induced inflammation can obstruct the main airway. Monitor patients closely between the laser light therapy and the mandatory debridement bronchoscopy for any evidence of respiratory distress.
Esophageal Strictures: Esophageal strictures can occur.
Hepatic and Renal Impairment: Patients with hepatic or renal impairment may need longer precautionary measures for photosensitivity.
Thromboembolism: Thromboembolic events can occur.
Embryo-Fetal Toxicity: May cause embryo-fetal toxicity. Advise females of reproductive potential of the potential risk to a fetus and to use effective contraception.
MOST COMMON ADVERSE REACTIONS reported during clinical trials (>10% of patients) are:
Esophageal Cancer: Anemia, pleural effusion, pyrexia, constipation, nausea, chest pain, pain, abdominal pain, dyspnea, photosensitivity reaction, pneumonia, vomiting, insomnia, back pain, pharyngitis.
Obstructing Endobronchial Cancer: Dyspnea, photosensitivity reaction, hemoptysis, pyrexia, cough, pneumonia.
Superficial Endobronchial Tumors: Exudate, photosensitivity reaction, bronchial obstruction, edema, bronchostenosis.
High-Grade Dysplasia in Barrett’s Esophagus: Photosensitivity reaction, esophageal stenosis, vomiting, chest pain, nausea, pyrexia, constipation, dysphagia, abdominal pain, pleural effusion, dehydration.
Other Photosensitizing Agents: May increase the risk of photosensitivity reaction.
Lactation: Because of the potential for serious adverse reactions in the breastfed infant, advise patients that breastfeeding is not recommended during treatment with PHOTOFRIN and for 5 months after the last dose.
Please see full Prescribing Information for PHOTOFRIN (porfimer sodium) for Injection at: www.photofrin.com.
FOR MORE INFORMATION about PHOTOFRIN, or if there are any questions regarding the information provided, visit www.photofrin.com or please contact the Medical Information Department at 1-866-248-2039. You are encouraged to report negative side effects of prescription drugs to the FDA. Visit www.fda.gov/medwatch, or call 1-800-FDA-1088.
PHOTOFRIN® and OPTIGUIDE® are registered trademarks of Concordia Laboratories Inc.
Pinnacle Biologics™ and the logo of Pinnacle Biologics™ are trademarks of Pinnacle Biologics, Inc.
PHOTOFRIN® is distributed in the United States by Pinnacle Biologics, Inc., Bannockburn, IL 60015
All rights reserved.
Please see accompanying full Prescribing Information for Photofrin®